- A fiber optic cable consists of a bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting data onto light waves.
- It is a high speed data transmission medium, can send data in the speed of light.
- The receiving end of a fiber optic transmission translates the light pulses into binary values, which can be read by a computer.
- It uses in commercial business, governments, the military, now it also used by internet service provider.
Types
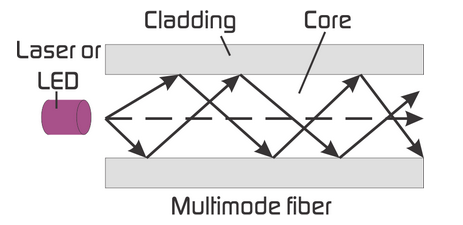
Multi-mode fiber
- In a multi-mode fiber, the core diameter is much bigger than the wavelength of the transmitted light.
- It can carry multiple light rays or modes concurrently, each at a slightly different reflection angle within the optical fiber core.
- Multi-mode fiber transmission is used for relatively short distances because the modes tend to disperse over longer lengths.
- Because of its high capacity and reliability, multi-mode optical fiber generally is used for backbone applications in buildings.
Single-mode fiber
- A type of fiber with a small core that allows only one mode of light to transmit.
- There more information can be transmitted per unit of time.
- Single-mode fiber allows for a higher capacity to transmit information.
- Single-mode cable used by telephone industries for long distance telecommunication.
Advantages
- Extremely high bandwidth
- It can also be run in electrically noisy environments without concern as electrical noise will not affect fiber.
- An optical fiber offers low power loss.
- Fiber optic cables are much thinner and lighter than metal wires.
- Fiber do not lose any light, therefore the transmission is also secure and cannot be disturbed.
- Lightness and small size of the cable, capable of carrying a large number of signals.
- As optical fiber has no electrical conductivity, therefore grounding and protection are not necessary.
- Easily can install.
Disadvantages
- The glass can be affected by various chemicals including hydrogen gas.
- Transmission on optical fiber requires repeating at distance intervals.
- Fibers can be broken or have transmission losses when wrapped around curves of only a few centimeters radius.
- Special test equipment is required.
- Optical fibers are more costly.
Applications
My notes








No comments: