- Data encryption translates data into another form or code, so that only people with access to a secret key (formally called a decryption key) or password can read it.
- Normal text is called plain text after encryption the text is referred as cipher text (means a secret code).
- The cipher text only can read after decrypted using a decryption key.
- Currently encryption is one of the most popular and effective data security methods used by organisations.
Types
Symmetric key
- In symmetric key schemes the encryption and decryption keys are the same.
- The sender must exchange the encryption key with the recipient before he can decrypt it.
- Symmetric key encryption is faster than public key encryption.
- Like in companies they are securely distribute and manage huge quantities of keys.
Public key
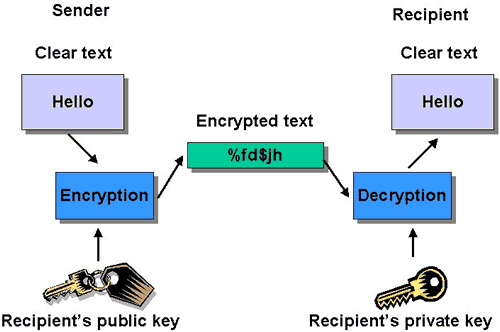
- Public key encryption uses two different keys, one public and one private.
- The public key shared with everyone, but the private key must be protected.
- Only the receiving party has access to the decryption key that enables messages to be read.
- It is used to secure sensitive data, especially when it is sent over an insecure network like the internet.
Advantages
- Complete data protection.
- Unauthorized access protection.
- Move data securely.
- Identity theft prevention.
- Security across multiple devices.
Disadvantages
- Forgetting passwords.
- Developing a false sense of security.
- Raising suspicious.
Uses
- Encryption has long been used by military and governments to facilitate secret communication.
- It is now commonly used in protecting information within many kinds of civilian systems. For example, the Computer Security Institute reported that in 2007.
- Encryption is also used to protect data in transit, for example sending data via internet, mobile telephone, wireless microphones, Bluetooth devices etc.




No comments: